Originally published February, 2017 and updated May, 2019
Forcing a Group Policy Update
- I would also try logging into the device as another user and run the gpupdate /force and see if you get the same issues. This will also allow you to see if it is a user issue, device issue or server issue. Please let me know how you go with this so I can provide more solutions for you to try.
- To force update all policies, run the command: gpupdate /force The commands above will update both User Group Policies and Computer Group Policies simultaneously. Also, it is possible to force update Computer group policies or User Group policies individually.
Gpupdate /force exit. I can go in and do the command and it works just fine. What Im really trying t supress is to not have to go to every individual machine login and do it. It takes more time.

Imagine that you get a phone call from the security specialist who handles your firewalls and proxy servers. He tells you that he has added an additional proxy server for users going to the internet. You add a new GPO that affects all users so they can use the new proxy server via Internet Explorer. Usually, it takes between 90 and 120 minutes for a new GPO to be applied, but you need the new settings to be applied right now, and you cannot tell your users to log off and log back in to apply them. In cases like these, you might want to bypass the normal wait time before background policy processing kicks in. You can do so using the command prompt, the Group Policy Management Console (GPMC) or PowerShell.
Forcing a Group Policy Update using the Command Prompt
Your first option is to run a simple command that tells the client to skip the normal background processing interval and update all new or changed GPOs from the server right now. However, you must physically trot out to each user machine and enter the gpupdate command, thereby refreshing the Group Policy object, along with any other new or changed GPOs, manually.
Note that running the gpupdate command with no parameters will refresh both the User and the Computer halves of the Group Policy objects. To refresh just one half or the other, use this syntax:
gpupdate /Target:Computer, /Target:User
Running gpupdate while a user is logged on to a machine immediately gives Windows the new GPO settings (assuming, of course, that the domain controller has the replicated GPO information). Black panther 4k movie free download.
In Windows XP and later, Fast Boot, Software Distribution and Folder Redirection are enabled by default, so settings are processed only at the next logon time. If you use the right switches, gpupdate can figure out if newly changed items require a logoff or reboot to be active:
- Running gpupdate with the /Logoff switch will figure out if a policy change in Active Directory requires the user to log off. If not, the new settings are applied immediately; if so, the user will automatically be logged off and the Group Policy settings will be applied when they log back in.
- Similarly, if Fast Boot is enabled, a restart is required to apply GPOs that have Software Distribution settings. Running gpupdate with the /boot switch will figure out if a policy has something that requires a reboot and automatically reboot the computer. If the updated GPO does not require a reboot, the GPO settings are applied and the user remains logged on.
Both the /Logoff and /boot switches are optional.
The discussion so far applies only to new GPOs and changes to existing ones. However, sometimes you might want to apply all GPOs to a computer — not just new or changed GPOs but old ones as well. In that case, you need to use the /force switch with gpupdate, as follows:
gpupdate /force
Other options are available in conjunction with /force, including:
- /Logoff — Log the user off after the Group Policy settings have been updated.
- /Sync — Change the foreground (startup/logon) processing to synchronous.
- /Boot — Restart the machine after the Group Policy settings are applied.
Forcing a Group Policy Update using the Group Policy Management Console
As an alternative to the command-line tools, you can force a Group Policy update using the Group Policy Management Console (GPMC). GPMC is included with every Microsoft Windows Server since Windows Server 2008; you can also get it by installing Remote Server Administration Tools (RSAT).
To force a GPO to be applied, take these simple steps:
- Open
- Link the GPO to an OU.
- Right-click the OU and choose the 'Group Policy Update' option.
- Confirm the action in the Force Group Policy Update dialog by clicking 'Yes'.
Forcing a Group Policy Update using PowerShell

Since Windows Server 2012, you can force a Group Policy refresh using the PowerShell cmdlet Invoke-GPUpdate. This command can be used for Group Policy remote update of Windows client computers. You will need to have both PowerShell and the Group Policy Management Console installed.
The big bang theory season 8 full download. Here is an example of using this cmdlet to force an immediate Group Policy update on a particular computer:
The RandomDelayMinutes 0 parameter ensures that the policy is updated instantly. The only downside to using this parameter is that the users will get a cmd screen pop-up.
If you want to force an update on all computers, run these commands:
This code will get all computers from the domain, put them into a variable and run the commands for each object.
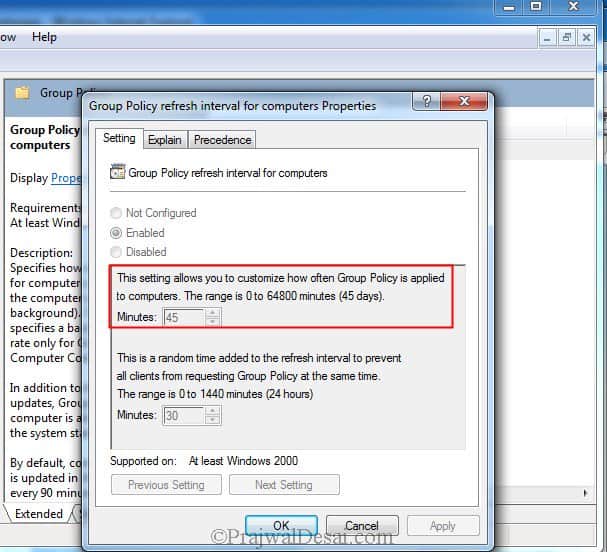
GPO Background Refresh
All Group Policy clients process GPOs when the background refresh interval comes to pass — but they process only those GPOs that are new or have changed since the last time the client requested them.
However, for security settings, the Group Policy engine works differently. It asks for a special background refresh just for security policy settings. This is called the background security refresh and is valid for every version of Windows Server. Every 16 hours, each Group Policy client asks Active Directory about all the GPOs that contain security settings (not just the ones that have changed) and reapplies those security settings. This ensures that if a security setting has changed on the client (behind the Group Policy engine's back), it's automatically reverted to the proper setting within 16 hours.
Background Refresh Process for Local GPOs
Gpupdate /force Powershell Command
If users are local administrators of their Windows machines, they have total control to go around the Group Policy engine processes and can make changes to local policies — changes that could nullify a policy you've set with a GPO, including things on the system that shouldn't be changed. To avoid this issue, you should give local administrator accounts only to some privileged users that cannot work with local administrator rights or give local admin rights only to those applications that privileged users need to run. You should never give regular users administrative rights.
Mandatory Reapplication of Non-security Group Policy Settings
As described above, the background security refresh updates all security-related policy settings every 16 hours. But sometimes you also need to force non-security settings to be applied, even if the GPOs on the servers haven't changed in order to fix exploits that aren't specifically security related.
You can choose to mandate the reapplication of the following areas of Group Policy during each initial policy processing and background refresh:
- Registry (Administrative Templates)
- Internet Explorer Maintenance
- IP Security
- EFS Recovery Policy
- Wireless Policy
- Disk Quota
- Scripts
- Security
- Folder Redirection
- Software Installation
- Wired Policy
Gpupdate Force Command
Conclusion
To recap, when you change a GPO in Active Directory, it will be automatically applied at the next refresh interval; you can also force a refresh to apply it immediately to your client systems. As an extra safety measure, you can set up mandatory reapplication to ensure that certain Group Policy settings are always reapplied, even if they have not changed. This enables you to revert any unwanted changes made by local administrators.
When you make a change to a Group Policy Object (GPO), thechange takes place on a Windows 2000 domain controller.The change is replicated to all other domain controllers in theActive Directory. All Windows computersin the Active Directory check for modifications to GPOs at regularintervals. If they find changes, they apply them during the nextinterval.
If you need to apply the change immediately, you can use thefollowing command to trigger the updating process:
This command compares the currently applied GPO to the GPO that islocated on the domain controllers. If nothing has changed since thelast time the GPO was applied, then the GPO is skipped.
If Windows accepts the request, it will display the followingmessage:

Imagine that you get a phone call from the security specialist who handles your firewalls and proxy servers. He tells you that he has added an additional proxy server for users going to the internet. You add a new GPO that affects all users so they can use the new proxy server via Internet Explorer. Usually, it takes between 90 and 120 minutes for a new GPO to be applied, but you need the new settings to be applied right now, and you cannot tell your users to log off and log back in to apply them. In cases like these, you might want to bypass the normal wait time before background policy processing kicks in. You can do so using the command prompt, the Group Policy Management Console (GPMC) or PowerShell.
Forcing a Group Policy Update using the Command Prompt
Your first option is to run a simple command that tells the client to skip the normal background processing interval and update all new or changed GPOs from the server right now. However, you must physically trot out to each user machine and enter the gpupdate command, thereby refreshing the Group Policy object, along with any other new or changed GPOs, manually.
Note that running the gpupdate command with no parameters will refresh both the User and the Computer halves of the Group Policy objects. To refresh just one half or the other, use this syntax:
gpupdate /Target:Computer, /Target:User
Running gpupdate while a user is logged on to a machine immediately gives Windows the new GPO settings (assuming, of course, that the domain controller has the replicated GPO information). Black panther 4k movie free download.
In Windows XP and later, Fast Boot, Software Distribution and Folder Redirection are enabled by default, so settings are processed only at the next logon time. If you use the right switches, gpupdate can figure out if newly changed items require a logoff or reboot to be active:
- Running gpupdate with the /Logoff switch will figure out if a policy change in Active Directory requires the user to log off. If not, the new settings are applied immediately; if so, the user will automatically be logged off and the Group Policy settings will be applied when they log back in.
- Similarly, if Fast Boot is enabled, a restart is required to apply GPOs that have Software Distribution settings. Running gpupdate with the /boot switch will figure out if a policy has something that requires a reboot and automatically reboot the computer. If the updated GPO does not require a reboot, the GPO settings are applied and the user remains logged on.
Both the /Logoff and /boot switches are optional.
The discussion so far applies only to new GPOs and changes to existing ones. However, sometimes you might want to apply all GPOs to a computer — not just new or changed GPOs but old ones as well. In that case, you need to use the /force switch with gpupdate, as follows:
gpupdate /force
Other options are available in conjunction with /force, including:
- /Logoff — Log the user off after the Group Policy settings have been updated.
- /Sync — Change the foreground (startup/logon) processing to synchronous.
- /Boot — Restart the machine after the Group Policy settings are applied.
Forcing a Group Policy Update using the Group Policy Management Console
As an alternative to the command-line tools, you can force a Group Policy update using the Group Policy Management Console (GPMC). GPMC is included with every Microsoft Windows Server since Windows Server 2008; you can also get it by installing Remote Server Administration Tools (RSAT).
To force a GPO to be applied, take these simple steps:
- Open
- Link the GPO to an OU.
- Right-click the OU and choose the 'Group Policy Update' option.
- Confirm the action in the Force Group Policy Update dialog by clicking 'Yes'.
Forcing a Group Policy Update using PowerShell
Since Windows Server 2012, you can force a Group Policy refresh using the PowerShell cmdlet Invoke-GPUpdate. This command can be used for Group Policy remote update of Windows client computers. You will need to have both PowerShell and the Group Policy Management Console installed.
The big bang theory season 8 full download. Here is an example of using this cmdlet to force an immediate Group Policy update on a particular computer:
The RandomDelayMinutes 0 parameter ensures that the policy is updated instantly. The only downside to using this parameter is that the users will get a cmd screen pop-up.
If you want to force an update on all computers, run these commands:
This code will get all computers from the domain, put them into a variable and run the commands for each object.
GPO Background Refresh
All Group Policy clients process GPOs when the background refresh interval comes to pass — but they process only those GPOs that are new or have changed since the last time the client requested them.
However, for security settings, the Group Policy engine works differently. It asks for a special background refresh just for security policy settings. This is called the background security refresh and is valid for every version of Windows Server. Every 16 hours, each Group Policy client asks Active Directory about all the GPOs that contain security settings (not just the ones that have changed) and reapplies those security settings. This ensures that if a security setting has changed on the client (behind the Group Policy engine's back), it's automatically reverted to the proper setting within 16 hours.
Background Refresh Process for Local GPOs
Gpupdate /force Powershell Command
If users are local administrators of their Windows machines, they have total control to go around the Group Policy engine processes and can make changes to local policies — changes that could nullify a policy you've set with a GPO, including things on the system that shouldn't be changed. To avoid this issue, you should give local administrator accounts only to some privileged users that cannot work with local administrator rights or give local admin rights only to those applications that privileged users need to run. You should never give regular users administrative rights.
Mandatory Reapplication of Non-security Group Policy Settings
As described above, the background security refresh updates all security-related policy settings every 16 hours. But sometimes you also need to force non-security settings to be applied, even if the GPOs on the servers haven't changed in order to fix exploits that aren't specifically security related.
You can choose to mandate the reapplication of the following areas of Group Policy during each initial policy processing and background refresh:
- Registry (Administrative Templates)
- Internet Explorer Maintenance
- IP Security
- EFS Recovery Policy
- Wireless Policy
- Disk Quota
- Scripts
- Security
- Folder Redirection
- Software Installation
- Wired Policy
Gpupdate Force Command
Conclusion
To recap, when you change a GPO in Active Directory, it will be automatically applied at the next refresh interval; you can also force a refresh to apply it immediately to your client systems. As an extra safety measure, you can set up mandatory reapplication to ensure that certain Group Policy settings are always reapplied, even if they have not changed. This enables you to revert any unwanted changes made by local administrators.
When you make a change to a Group Policy Object (GPO), thechange takes place on a Windows 2000 domain controller.The change is replicated to all other domain controllers in theActive Directory. All Windows computersin the Active Directory check for modifications to GPOs at regularintervals. If they find changes, they apply them during the nextinterval.
If you need to apply the change immediately, you can use thefollowing command to trigger the updating process:
This command compares the currently applied GPO to the GPO that islocated on the domain controllers. If nothing has changed since thelast time the GPO was applied, then the GPO is skipped.
If Windows accepts the request, it will display the followingmessage:
For more about this command, from the Start menu,select Help and Support, and then search on grouppolicy management.
